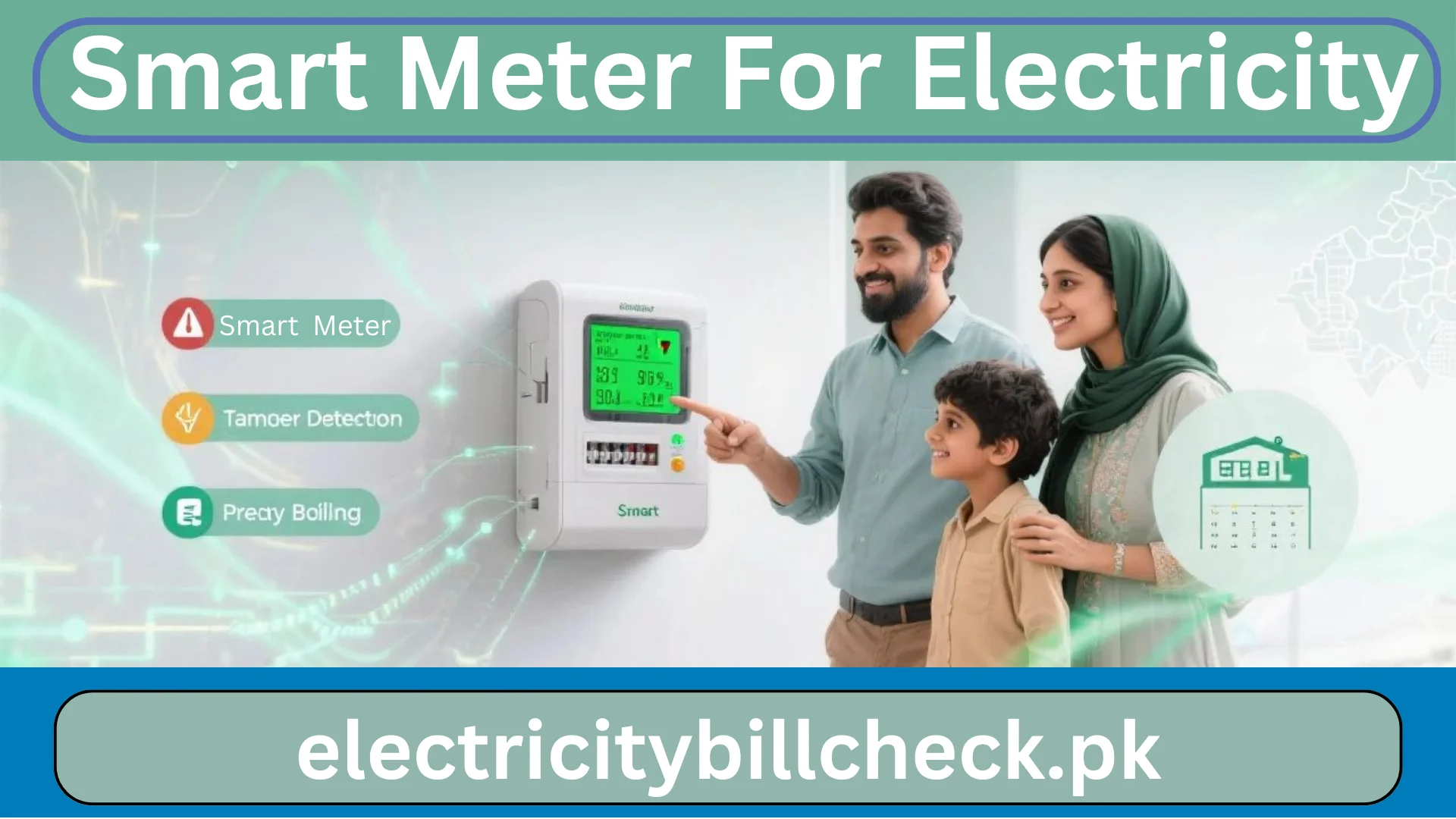
Smart Meter For Electricity
A smart meter is an advanced electronic device for measuring electricity usage through automatic digital communication to consumers and utilities. Unlike traditional analog meters, which require manual readings,Smart Meter For Electricity provide information almost in real time, allowing dynamic monitoring and management of electricity consumption. Smart meters are creating a revolution in the electricity consumption monitoring space by allowing real-time data transfer and efficient energy management across the globe.
Smart meters are a crucial component of smart meter mepco grid development, employing digital communications technology that controls and optimizes the generation, distribution, and consumption of electricity. Utilities reduce operational costs by using smart meters, as these will eliminate the need for manual readings and assist in quick outage and theft detection. On the consumer’s side, smart meters allow energy consumption baselines that help to make intelligent energy choices and save on their bills.
How Smart Meter For Electricity Work?
Smart Meter For Electricity continuously measure electricity parameters using embedded sensors and communication modules. These meters can wirelessly transmit data via cellular networks, Wi-Fi, or power line communication (PLC). The data is sent to the utility provider at regular intervals without the need for manual reading of the meter.
Consumers are usually given real-time consumption data using in-home displays or through mobile apps, allowing them to track usage, patterns, and behavioral adjustments to save on energy and costs. They also warn of possible tampering, power outages, and voltage fluctuations by sending alerts to users and utility companies for immediate action.
Smart Electricity Meter Features
Smart Meter For Electricity offers much more than simple measurement:
Remote Real-Time Monitoring: Utilities and consumers alike can access consumption data at any time they want.
Anti-Tampering: The technology includes magnetic interference detection, cover removal alarms, and reverse current monitoring.
Automatic Time-of-Use Tariff Switching: Automatically accounts for the consumption of energy during peak and off-peak periods for proper billing.
Load Monitoring and Alerts: Alerts of overloads, voltage irregularities, and low power factor for hazard mitigation.
Power Outage Notification: Alerts the users immediately upon the loss of power and upon restoration.
Remote Firmware Upgrades: Facilitate utilities upgrading the meter software without physical visits.
Prepaid Billing: Some smart meters have prepaid billing options that allow users to better manage their budget.
Smart Meter Specifications Technical Standards and Requirements
Smart Meter For Electricity precision, endurance and interoperability, they are expected to meet strict technical standards. A common agreement exists with far-reaching international alignment with IEC 62052-11 (general requirements), IEC 62053-21 (accuracy class), and IEC 62056 (communication protocols).
More Smart Meter Specifications:
Accuracy Class: Class 1.0 or better (readings of the meter are considered to be in error by less than one percent of actual consumption).
Voltage Rating: 220-240V for single-phase meters and 380-415V for three-phase meters.
Current Range: Residential meters are typically rated from 5A to 60A, while commercial meters have higher ratings.
Communication Interface: Support for DLMS/COSEM, Modbus, or proprietary wireless protocols.
Environmental Ratings: Designed to function from -20°C to +60°C, with specific protections against dust and moisture (IP54 or above).
Display: The display is an LCD or LED of higher resolutions showing consumption, voltage, current, power factor, and error codes.
Tamper Detection: Sensors for detection of external magnetic fields, reverse wiring, and hard tampering means to affix.
Power Supply: Usually powered from mains supply, featuring auxiliary battery back-up for certain data retention during outages.
Smart Meter Implementation Process Step-by-Step Guide
In considering an upgrade, users would generally follow this process:
Contact Your Energy Supplier: Contact them directly to explore their offering. Availability will depend on where you are and your supplier’s rollout schedule.
Receive Confirmation: Your supplier will give you which date that will be scheduled for your installation.
Book Installation Date: A date as well as time will be provided to you to choose a convenient time when a technician will come to install the unit.
Pre-Installation Reminder: Installers sometimes send a reminder on the intended installation date.
Smart Meter Installation: Highly trained technicians come to fit the new meter, safety check and demo test it, and show you how to use the device and any display devices that you might be using in the home.
Smart Meters vs. Traditional Meters
It offers a life-changing advantage over traditional one:
Improved Accuracy errors in billing were reduced, and estimated bills were eliminated. Consumers were empowered by real-time data in making energy decisions. Meter Reading and Manual Billing services are common services consumed by most utilities. Advanced tampering alarms curb electricity theft, a serious problem in Pakistan. Supports net metering, where the excess solar power generated by consumers can be sold back to the grid. Savings in paper usage due to electronic billing and fewer visiting services. Utility load data optimization for generation improvement measures the reduction of outages.

Features and Consumer Benefits
The Smart Meter Mepco initiative is a meaningful section of MEPCO’s ambition of modernizing electricity distribution throughout southern Punjab. The program aims to substitute conventional analog meters with advanced smart meters to promote accurate billing, curb electricity theft, and improve customer service. The benefits to MEPCO consumers are far-reaching. Accurate billing means no estimated charges; therefore, disputes are minimized, allowing customers to naturally pay for their actual electricity consumption. With the Mepco Smart app, consumers can see their real-time consumption data and use it to monitor their usage closely and manage their electricity expenses. The program also sends timely notifications regarding scheduled load shedding, thus empowering them to plan before power outages to reduce inconvenience.
Conclusion
Smart meters have a remote communication feature that notifies users if the appliance is tampered with, provides information on prepaid billing, and has infringement detection and remote monitoring features. These high-tech benefits make it one of the most fascinating tools for optimizing energy consumption by utility companies and consumers. Pakistan is making them more accessible to households under the initiative Smart Meter Mepco, which will create efficient and transparent practices. Smart meter knowledge, understanding what is smart meter, features, specifications, and installation process will help consumers take control of their energy consumption for a sustainable future.